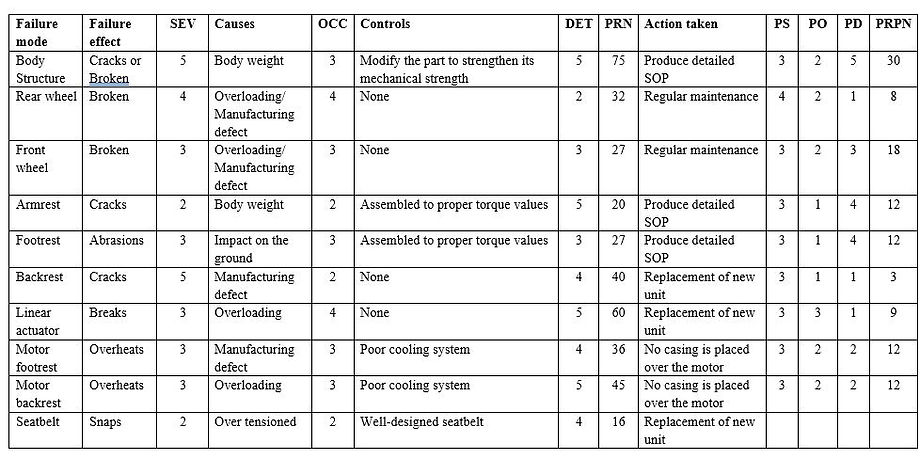
Failure mode
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a structured approach to find potential failures that might exist within the design of a process or product. The FMEA is splitted into two components which are failure modes and effect analysis. Failure modes are known as the likely condition that the process or product will fail due to defectiveness of components. Effect analysis is defined as the study on effect of defectiveness of the components towards users and operators. FMEA is also categorized into two distinguished categories which Design FMEA and Process FMEA.
In this project, Design FMEA will be used. It explores the possibility of reduction of product lifespan, malfunction, and safety regulations that are derived from geometry, tolerances, interfaces with other components and material properties. Design FMEA is used to provide method of quantitative analysis of risk, compare design concepts and redesign products and documents safety review in easy-to-read table.
The steps and procedures to carry out the FMEA are relatively direct. The identification of failures is important part of the FMEA analysis as it functions as the roots for the analysis. This FMEA involve several tables to give the appropriate ratings towards the potential failures based on its severity, occurrence, and detection.
Procedure of FMEA
Brainstorm all the possible failure modes.
List down all potential failure modes and its consequences.
Identification
Identify the function model, current control to counter the problem and the actions recommended to be taken to properly avoid to the failure modes.
Severity scores (SEV)
Gives a rating on the severity of failure using the scale of 1 to 10, higher number means the failure is more severe.
Apportion Occurrence scores (OCC)
Each potential cause will have one OCC score based on actual data. Using the same scale of 1 to 10, score of 1 means the least significant and 10 means most significant.
Easiness of Detection (DET)
From the scale of 1 to 10, the appropriate score is given based on how likely the failure will escape detection by the planned control system. If it is low, lower score should be given.
Calculation Risk Priority Number (RPN)
RPN is the measure of risk. Using this formula to determine the RPN: RPN = SEV x OCC x DET.
Determination of action plans to be taken.
Based on RPN calculated, the best possible measure is determined to completely eliminate the failure mode.
Recalculation of RPN
Based on above step (vii), the revised RPN value should be lower than the RPN.
This FMEA emphasise on the prevention to reduce the possibility of potential failures to occurred in the design project. However, the risk of failure is hard to be completely eliminated but it can be reduced to an acceptable level with proper mitigation measured